The integration of drone technology into cadastral surveying marks a significant development in this field of geographic surveying and mapping. Intelligent mapping enabled by drones can quickly cover large areas, capture large amounts of high-resolution data, and generate detailed 3D maps and land models, which are critical for accurate cadastral records.
What is cadastral surveying?
Cadastral surveys play an important role in shaping society by clearly delineating plot boundaries and helping everyone know who owns what and how much it is worth.
Cadastral surveying focuses on land tenure, ownership and rights and plays a vital role in land administration and management.
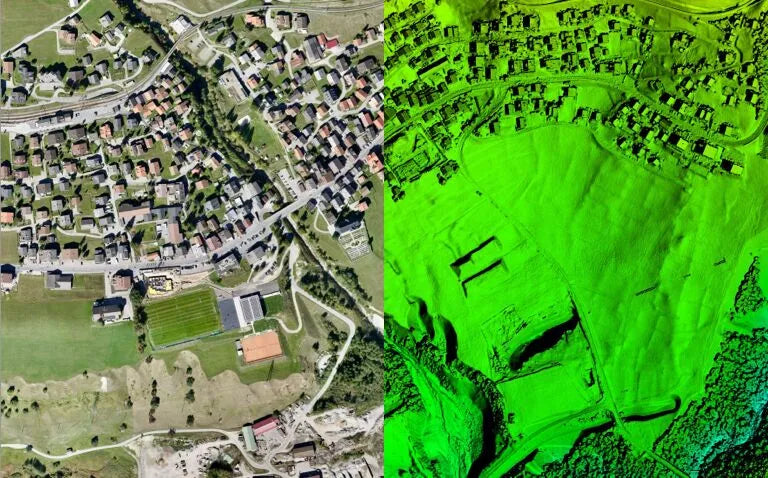
Traditional cadastral surveying vs drone intelligent surveying and mapping
A traditional cadastral survey would require a surveyor to carry equipment such as a total station, electronic range finder and GPS receiver, establish a baseline and measure everything.
Drone intelligent surveying uses advanced drone sensors and imaging technology to bring speed, accuracy and safety to a whole new level. The high-resolution data obtained by drone cameras is more detailed and precise than that obtained by older methods, while minimizing the risks and physical challenges associated with traditional survey methods.
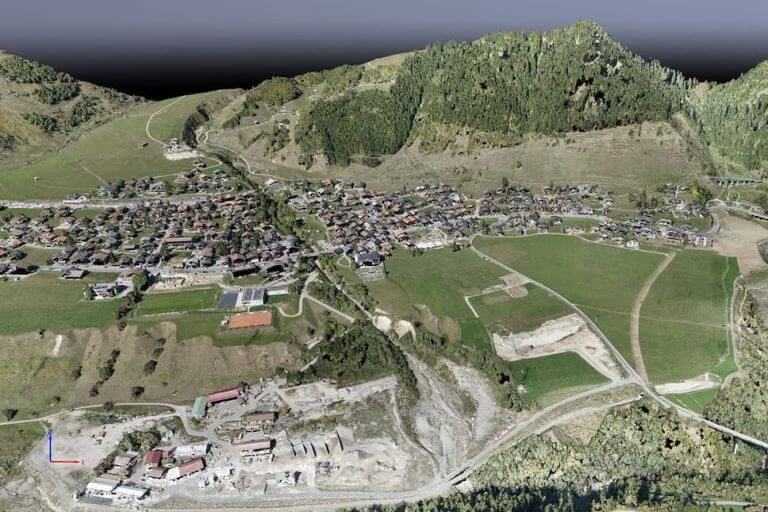

Drone technology in cadastral surveying
Drone type
Land survey drones can be roughly divided into two categories:
Quadcopters Drones, known for their ability to hover and maneuver into tight spots, are great for when you need to get a really close look at an area.
Fixed-wing drones are suitable for large-scale surveys due to their longer flight times and ability to cover more ground quickly.
The choices the team made depended on project requirements, such as the size of the area to be measured, the level of detail required and the flexibility the drone needed. Then, further improvements will be made in terms of the drone’s flight range, battery capacity and safety features.
Sensors used
A drone's sensor technology often plays a more critical role than the drone's construction. While there are different sensor technologies, lidar (light detection and ranging) and photogrammetry cameras are the most common. LiDAR sensors create a 3D point cloud that represents the terrain, while photogrammetry cameras use a series of photos to generate a 3D image of the area.
What kind of drone is suitable for cadastral survey?

Drones used in cadastral surveys can encounter large survey areas, difficult or steep terrain, large altitude differences, adverse weather conditions or lack of flat surfaces required for takeoff and landing, etc. This also illustrates the importance of drone performance.
Drone cadastral surveying needs to consider the flight duration of the drone, the image output quality of the drone, and the measurement accuracy of the RTK drone. Likewise, your budget and preference for your drone are equally important!
Among Autel drones, you can choose the Autel RTK drone series for cadastral surveying. This includes Autel EVO II Pro RTK V3, Autel EVO II 640T RTK V3, Autel MAX 4T with RTK.
6 benefits of using drones in cadastral surveying

1. Improve efficiency
Drones can cover large areas quickly and easily, reducing the time spent on survey missions. They provide real-time monitoring and data accuracy, minimizing errors and the need for rework.
2. Cost-effective data collection
Drones reduce reliance on expensive equipment and manual labor, resulting in significant cost savings. It's certainly better than lugging around a theodolite and GPS receiver, installing them at multiple sites.
3. Accurate, precise and fast data processing
Using drones, surveyors can create detailed 3D models and maps of target areas. This can then be processed using different types of drawing software depending on the desired results. Real-time analytics and data visualization capabilities improve decision-making by providing up-to-date and reliable information.
4. Improved security measures
There is no longer a need to send surveyors into hazardous locations. Drones can fly over tall buildings or steep cliffs, keeping everyone safe.
5. Diverse terrain coverage
Whether it’s rocky hills or dense forests, drones can handle it. Modern units include obstacle avoidance as a standard feature and can navigate challenging landscapes, ensuring that no place is uncharted.
6. Remote access and monitoring
This enables immediate access to data and enables fast decision-making, thereby enhancing project oversight. With integrated cloud capabilities, relevant stakeholders can become part of the entire process.
Challenges cadastral surveyors face when using drones

Regulations: For commercial flying drones, surveyors must obtain the necessary permits and licenses before operating the drone and strictly abide by laws and regulations.
Weather dependence: Situations such as heavy rain or strong winds can seriously affect drone flight.
Equipment maintenance: As an intelligent electronic product, drones have higher maintenance costs. Please purchase insurance for your drone.
Technical expertise: Surveyors must be adept at operating commercial drones and interpreting the data they produce. The 3D maps generated for drone imagery must be able to be reviewed and interpreted.
Limited flight time: Drone flight time is limited by battery limitations and power limitations, which can be challenging when conducting large-scale surveys or covering wide areas.
Safety Concerns: While drones are safer for surveyors, they still need to be flown responsibly to avoid any collisions or collisions with other objects or worse, people.
The future of drone land surveying
The future of drone cadastral surveying depends on continued advancements in drone technology. Enhanced sensors, improved flight autonomy, and the integration of artificial intelligence are expected to further refine measurement capabilities. These upgrades are designed to push the boundaries of what is possible, making measurements more precise, efficient and versatile than ever before.








